What effect does the temperature have on the selection of grease?
March 09, 2024
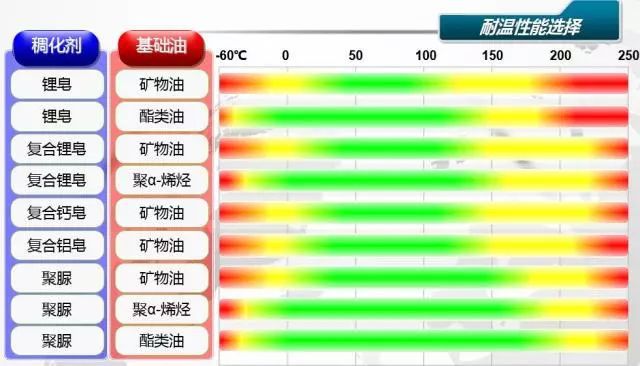
What effect does the temperature have on the selection of grease? When choosing a grease, the temperature range used is a factor we need to consider. Greases have a certain temperature range, and different greases have different temperature ranges. The composition of grease is the Base Oil, thickener, additive, the use temperature of grease is also related to these three components, for a certain grease, the manufacturer will give a maximum use temperature and minimum use temperature, the user should remember, when choosing, the user needs to consider the highest and lowest temperature of the lubrication part (generally the lowest temperature when starting). 1. Minimum operating temperature of grease The hardness of the grease will increase when the temperature drops, affecting the normal transmission, causing the grease to not fully reach the lubrication point, and the lack of lubrication when the machine is cold started. The minimum service temperature of the grease must be higher than the lowest ambient temperature at cold start, and at lower temperatures (such as close to -30 ° C), synthetic greases should be used, such as greases using PAO as a base oil. The maximum use temperature of grease: there is an indicator of the drop point of grease, but the drop point is not equal to the maximum use temperature, the maximum allowable use temperature of grease is generally 30 ° C ~ 50 ° C lower than the drop point, do not use excessive temperature, especially the high temperature for a period of time. If the grease exceeds the drop point, even if it cools down, the performance has been damaged and should not be used. 2. Performance of grease at high temperature The direct harm of the use of excessive temperature of lubricating oil is to accelerate oxidation deterioration, and generate acidic substances, it is worth noting that if the lubrication point appears local high temperature, it will also cause oxidation deterioration of grease, and gradually spread. Local high temperature may be caused by poor bearing installation, may also be caused by too much or insufficient grease, wrong oil selection, vibration, heavy load and other problems.
The oxidized grease will become darker, and the resulting acid will cause the thickener to decompose, causing the base oil to drain from the thickener. Grease is actually the thickened lubricating oil, and the thickener adsorbed the base oil like a sponge to avoid too much loss, so lubrication is mainly by oil lubrication. If the base oil is lost, although there is grease on the surface, the lubrication ability is almost no, and we can observe changes in the consistency of the grease during the oxidation process, such as hardening or thinning, and oil flow. Common greases are generally composed of lithium base thickeners and mineral base oils, which can meet the lubrication requirements of most ordinary working conditions. If there is a high temperature (above 60 degrees Celsius), the grease will accelerate the oxidation, when close to 90 degrees Celsius, the oxidation of ordinary grease seriously restricts the performance of the grease, in these cases, it is necessary to use better grease, generally using synthetic oil and high-grade thickener, such as complex lithium, polyurea, complex Calcium Sulfonate and other types of thickener. These greases perform better than ordinary greases at both general and high temperatures. In the range of use of grease, the temperature characteristics of grease are also different, as mentioned earlier, grease is mainly lubricated by base oil, if the base oil has good viscositytemperature characteristics (viscosity index is high), then in the process of temperature change, the viscosity is relatively stable. The classification of base oil is stipulated by the API, and there are currently five classifications, and it is necessary for users to understand the base oil composition of grease when purchasing. Although the main components of the grease are the base oil and the thickener, the base oil and the thickener are not affected by the same degree of temperature, in general, the base oil is relatively more affected by the temperature change, and for the consistency of the thickener, the consistency changes more slowly before reaching the drop point. Therefore, when purchasing grease, it is necessary to understand the performance of the base oil. 3. Low temperature performance of grease At low temperatures, the grease will become thicker, that is, the hardness will increase, and the low temperature performance of the grease is also directly related to the base oil. Just like cooking oil, liquid at room temperature, low temperature will reduce the flow or even stop the flow. At a certain temperature, the lubricating oil stops flowing, which is called the pour point, and the lubricating oil with a low pour point can be used at a lower temperature. The pour point of mineral oil is generally -20 ~ -30 ° C, but the pour point is generally required to be lower than the use temperature. Low temperature torque is one of the important indexes of low temperature performance of grease. At low temperature, grease thickens and hardness increases, which will have retarding effect on bearing. Low temperature torque is the degree to which the grease blocks the rotation of the rolling bearing at low temperature (below -20 ° C), and the low temperature torque of the grease is expressed by the average value of the starting torque and the torque after running for a period of time. The smaller the starting torque value of the grease measured at low temperature, the smaller the starting power consumption; On the contrary, if the low temperature starting torque of a grease is large. There may be a phenomenon of stuck bearings, not suitable for use at low temperatures. Therefore, in the purchase of grease, the use temperature of the lubrication point (the highest and lowest temperature) must be taken into account, the permissible use temperature range of grease should include the use temperature range of grease and temperature related indicators, including the drop point, the highest use temperature, the lowest use temperature, the pour point of the base oil, low temperature torque, the viscosity index of the base oil and other indicators.