
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
Since it is not easy to attach the polar group directly to the hydrocarbon group, except in the case of olefns that are used to make DVMs, the need for a connecting group or a link arises. Although many such groups can be used, the two common ones are phenol and succinic anhydride. Olefn, such as polyisobutylene, is reacted either with phenol to form an alkylphenol or with maleic anhydride to form an alkenylsuccinic anhydride. The polar functionality is then introduced by reacting these substrates with appropriate reagents.

THE HYDROCARBON GROUP
Polyisobutylene is the most common source of the hydrocarbon group in polymeric dispersants. It is manufactured through acid-catalyzed polymerization of isobutylene. Figure depicts the mechanism of its formation. In Figure, polyisobutylene is shown as a terminal olefn, whereas in reality it is a mixture of various isomers. Those that predominate include geminally disubstituted (vinylidene), trisubstituted, and tetrasubstituted olefns. Figure shows their structure and the possible mechanism of their formation. Polyisobutylenes of structures I and II result from the loss of a proton from carbon 1 and carbon 3 of the intermediate of structure V. Polyisobutylenes of structures III and IV result from the rearrangement of the initially formed carbocation, as shown in Figure. The reactivity of these olefns toward phenol and maleic anhydride varies. In general, the more substituted the olefn, the lower the reactivity, which is a consequence of the steric factors. Similarly, the larger the size of the polyisobutyl pendant group, that is, the higher the molecular weight, the lower the reactivity. This is due to the dilution effect, which results from low olefn-to-hydrocarbon ratio. As mentioned earlier, polyisobutylene is the most commonly used olefn. One of the reasons for its preference is its extensive branching. This makes the derived dispersants to possess excellent oil solubility, in both nonassociated and associated forms. However, if the hydrocarbon chain in the dispersant is too small, its lubricant solubility greatly suffers. Because of this, the low-molecularweight components in polyisobutylene are not desired. This is despite their higher reactivity. These must be removed, which is carried out through distillation. Alternatively, one can minimize the formation of these components by decreasing the amount of the catalyst during polymerization and by lowering the polymerization reaction temperature.

A new class of dispersants derived from ethylene/α-OCP with an Mn of 300–20,000 has also been reported, primarily by the Exxon scientists. Such dispersants are claimed to have superior low- and high-temperature viscometrics than those of the polyisobutylene-derived materials. As mentioned earlier, dispersant polymers are derived from EPRs, styrene–butadiene copolymers, polyacrylates, PMAs, and styrene esters. The ethylene–propylene rubbers are synthesized by Ziegler–Natta catalysis. The styrene–butadiene rubbers are synthesized through anionic polymerization. Polyacrylates and PMAs are synthesized through polymerization of the monomers using free-radical initiators. Styrene esters are made by reacting styrene–maleic anhydride copolymer or styrene–maleic anhydride–alkyl acrylate terpolymer with alcohols, usually in the presence of a protic acid, such as sulfuric or methanesulfonic acid, catalyst. Since complete esterifcation of the anhydride is hard to achieve, the neutralization of the residual carboxylic acid anhydride is carried out by alternative means.
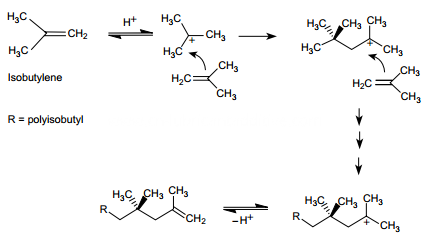
Acid-catalyzed polymerization of isobutylene.
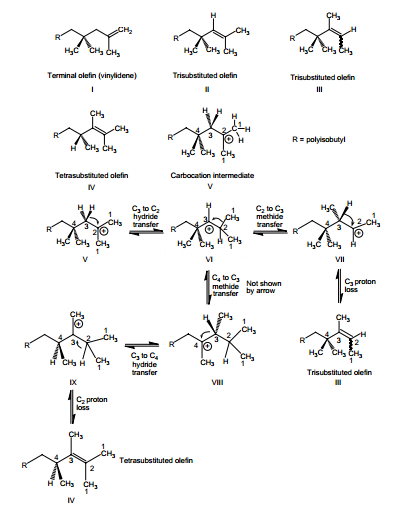
Polyisobutylene structures and the mode of their formation.
As a professional supplier of Lubricant Additive Component, we supply Ashless Dispersant , High Temperature Antioxidant, Rust Preventative Anti-rust Additive, Corrosion Inhibitor ZDDP, Pour Point Depressant , ect., to blend make different kinds of Additive Package ,such as Hydraulic Oil Additive Package, Gear Oil Additive Package, 4T Motorcycle Oil Additive Package, PCMO Gasoline Engine Oil Additive Package, HDEO Diesel Engine Oil Additive , ect.
Free feel to contact Email: sales@cn-lubricantadditive.com and Tel/WhatsApp: +86-13783582233 with any interest.
November 08, 2024
April 26, 2024
April 26, 2024
November 02, 2022
December 13, 2019
The viscosity grades of commonly used anti-wear hydraulic oil are 32 #, 46 # and 68 #. L-HN anti-wear hydraulic oil is suitable for low, medium and high pressure hydraulic systems of hydraulic...
Detergent dispersant is one of lubricant additive, which are mainly used in internal combustion engine oil. So why need use it? Because its main function is to keep the interior of the engine clean,...
Email to this supplier
November 08, 2024
April 26, 2024
April 26, 2024
November 02, 2022
December 13, 2019
Send Inquiry

Mr. James
Tel:0086-371-58651986
Fax:
Mobile Phone:+86 13783582233
Email:sales@cn-lubricantadditive.com
Address:No.11 Changchun Road, High-Tech Zone, Zhengzhou, Henan
Related Products List
Mobile Site


Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.